Site Selection for a Plant: Key Considerations
Plant Site Selection
II JAY SHRI KRISHNA II
Site selection is a critical strategic decision for any company planning to establish a new plant. It directly impacts the long-term viability, operational efficiency, and overall success of the venture. A well-considered site selection process ensures that the plant is located in an environment that supports its operations, minimizes costs and maximizes productivity.
A well-chosen site can lead to streamlined operations, reduced costs and enhanced market competitiveness. Conversely, a poorly selected site can result in increased expenses, logistical challenges and compliance issues. Therefore, a thorough evaluation of potential locations is crucial to ensure the long-term viability of the manufacturing facility.
Site Selection for a Plant: Key Considerations
 |
Site Selection Factors |
Site selection for a plant is a strategic, long-term decision that requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure the plant's operational success, technological viability and economic efficiency. Since such decisions are non-repetitive, they must incorporate a degree of forward-looking planning and alignment with corporate objectives.
Additionally, in India, site selection is often guided by the government’s industrial development policies. Here are some critical factors that will shape your site selection decision:
Critical Factors in Industrial Site Selection
Choosing a location for a new industrial facility is a high-stakes decision that dictates the project's long-term profitability and operational viability. It requires a delicate balance between engineering requirements, logistical costs and local regulations.
1. Proximity to Raw Materials and Markets
Reducing the distance between your plant and its primary input sources—as well as its final consumers—is the most effective way to lower transportation costs.
- Inbound Logistics: Ease of access for heavy-duty transport of raw materials.
- Outbound Logistics: Strategic placement near highways, rail links or ports for finished goods.
2. Infrastructure and Utility Availability
A plant cannot function without massive amounts of power, water and waste management capabilities.
- Power Grid Stability: Can the local grid handle the industrial load?
- Water Supply: Essential for cooling, processing and boiler feed water.
- Communication Networks: High-speed data links for modern SCADA and automation systems.
3. Topography and Soil Conditions
From a piping and civil engineering perspective, the ground itself is a factor.
- Soil Bearing Capacity: Determines if expensive piling is needed for heavy equipment like distillation columns or large storage tanks.
- Elevation: Affects drainage and gravity-flow piping design.
 |
Industrial Equipment Foundation & Pile Support System |
4. Regulatory and Environmental Compliance
Zoning laws and environmental impact assessments (EIA) can make or break a site.
- Zoning: Is the land legally designated for industrial use?
- Emissions & Waste: Are there strict local limits on air emissions or liquid effluent discharge?
Location Factor:
The location factor holds significant importance due to its long-term implications. A poor choice of location can lead to persistent challenges such as:
- Higher costs and investments
- Transportation inefficiencies
- Marketing difficulties
- Employee dissatisfaction
- Low availability of skilled professionals
- Frequent production interruptions and wastages
Relocating a plant after its establishment is difficult due to economic, political and social reasons. For example, social considerations may include employee welfare and job opportunities, while political factors might include regional development policies in a developing country like India. Therefore, meticulous planning is required to minimize risks.
Adequate Facilities to Consider:
1. District Classification
- Check if the plant’s license permits establishment in a no-industry district as per the government’s zoning policies.
2. Transportation Facilities
- Efficient and uninterrupted transportation is essential for raw materials and finished products.
1. Ensure proper connectivity through roads, ports and railheads.
2. Evaluate the feasibility of an in-plant rail siding based on the volume of materials to be handled.
- Airport connectivity is important for professional movement, especially in cases involving foreign collaborations.
3. Raw Material Availability
- Geographical proximity to raw material sources minimizes transportation expenses and maximizes supply chain reliability.
- Consider climatic conditions and specific requirements. For example:
1. Heat-sensitive components: Should be manufactured in cooler climates (e.g., Hindustan Photo Films located in Ooty to avoid the need for extensive air conditioning).
2. Plywood industry: Should avoid coastal zones to mitigate moisture-related product damage.
4. Manpower Availability
- Skilled and Semi-Skilled Labor: Local availability adds to efficient operations.
- Trade Unions and Stability: Assess the robustness and attitude of trade unions and labor stability.
- Training Cost: Proximity to training facilities can reduce costs and enhance workforce skills.
5. Industrial Infrastructure
- Includes railways, roadways, waterways, airways and communication facilities (telephone, microwave systems).
- Supporting services such as maintenance, repair workshops and plant services must be available in the vicinity.
- Vibrant existing infrastructure is preferred over infrastructure developed after plant commissioning.
6. Community Infrastructure
- A good community infrastructure is essential to attract qualified professionals.
- This includes quality schools, colleges, medical services, communication facilities and cultural/recreational opportunities.
7. Availability of Raw Water
- Proximity to a perennial source of water to meet plant and non-plant requirements is recommended.
- Drawing water solely from deep tube wells is not preferred due to potential depletion of groundwater resources.
8. Effluent Disposal
- A nearby effluent disposal facility, such as a nala, is advantageous.
- If unavailable, transporting effluent to a safe disposal area must address legal and ecological concerns.
9. Availability of Power
- Stable and uninterrupted power of the required magnitude, without voltage or frequency fluctuations, is critical.
- Nearness to a power facility reduces costs.
10. Availability of Industrial Gas
- Proximity to the gas pipeline network is advantageous for energy efficiency and pollution control.
- A gas-based captive steam power generation unit can provide uninterrupted power supply and support future expansions.
11. Site Size and Nature
- The plot area and topography should accommodate plant requirements, township facilities and future expansions.
- Preferably, the site should have natural soil with high load-bearing capacity to minimize foundation costs.
12. Ecology and Pollution
- The site should meet social and ecological obligations by maintaining a natural balance and minimizing pollution.
Qualitative Analysis: Weight-Cum-Rating Method
The weight-cum-rating method is a widely used technique to evaluate and rank potential sites. It involves the following steps:
1. Assign Weights:
- Identify Key Factors: Determine the most critical factors influencing the site selection decision. These factors could include proximity to raw materials, transportation infrastructure, labor availability, environmental impact and regulatory compliance.
- Assign Weights: Assign weights, to factors based on their relative importance. For instance, a factor like proximity to raw materials might be assigned a higher weight than a factor like recreational facilities.
2. Evaluate Potential Sites:
- Rating Scale: Develop a rating scale, typically a 0-5 scale, to assess each potential site against each factor.
- Factor-wise Evaluation: Evaluate each site on a factor-by-factor basis. For example, a site with excellent transportation infrastructure might receive a rating of 5, while a site with limited access might receive a rating of 2.
3. Calculate Points:
- Multiply Ratings by Weights: Determine the weighted score for each site by multiplying the assigned rating, for each factor by its corresponding weight.
- Summation: Sum up the weighted scores for all factors to obtain the total score for the site.
4. Total Score and Ranking:
- Compare Total Scores: Compare the total scores of all potential sites.
- Rank Sites: Rank the sites based on their total scores, with the highest-scoring site being the most preferred.
Example: Focusing on the Key Factors
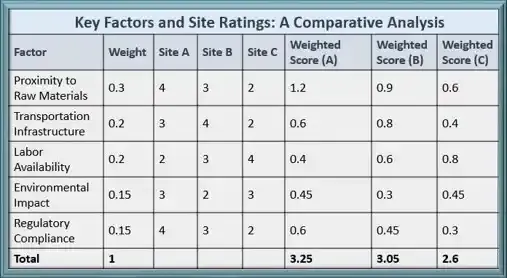 |
Focusing on the Key Factors |
In this example, Site A would be the preferred choice based on the highest total weighted score.
By systematically evaluating potential sites using the weight-cum-rating method, companies can make informed decisions that align with their strategic objectives and operational needs.
Industrial Site Selection Checklist
| Category | Checklist Item | Status (Yes/No/NA) | Priority (H/M/L) |
| Logistics | Proximity to primary Raw Material sources? | H | |
| Accessibility to major Highways/Expressways? | H | ||
| Availability of Rail Siding or nearby Railhead? | M | ||
| Distance to nearest Commercial Seaport/Airport? | M | ||
| Utilities | Stable Power Grid connection (capacity & voltage)? | H | |
| Proximity to Perennial Water Source (River/Lake)? | H | ||
| Natural Gas Pipeline access nearby? | M | ||
| Industrial Effluent/Waste disposal facility access? | H | ||
| Technical | Soil Bearing Capacity suitable for heavy foundations? | H | |
| Natural Topography (Flat vs. Sloped for drainage)? | L | ||
| Flood risk assessment and historical data check? | H | ||
| Regulatory | Land Zoning (Industrial vs. Agricultural/Residential)? | H | |
| Local Environmental Emission regulations check? | H | ||
| Availability of Government Subsidies/Tax Incentives? | M | ||
| Workforce | Availability of Skilled/Semi-skilled local labor? | M | |
| Housing and Community Infrastructure (Schools/Hospitals)? | L | ||
| History of Labor Stability and Trade Union activity? | M |
How to Use This Table:
1. Status Column: Mark whether the site meets the requirement.
2. Priority Column: H (High) indicates a "deal-breaker" factor, M (Medium) is important for cost and L (Low) is a "nice-to-have" feature.
3. Final Scoring: Use the Weight-Cum-Rating method discussed in the blog to quantify these results into a final score.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Why is site selection considered a non-repetitive strategic decision?
Site selection is a one-time, long-term commitment. Once a plant is built, the massive capital investment in civil foundations, piping networks and heavy machinery makes it economically and politically nearly impossible to relocate. Therefore, the decision must be right the first time.
2. How does soil bearing capacity affect the cost of a piping project?
If the site has poor soil bearing capacity, engineers must design expensive pile foundations to support heavy equipment like distillation columns or large storage tanks. This increases the civil costs and can complicate the design of underground piping and drainage systems.
3. What is the "Weight-Cum-Rating" method in site selection?
It is a qualitative analysis tool where decision-makers identify key factors (like power availability or labor cost), assign a "weight" based on importance, and then "rate" potential sites. The site with the highest total score is selected, ensuring an objective, data-driven choice.
4. Why is proximity to a perennial water source critical for industrial plants?
Many plants require large volumes of water for cooling towers, boiler feed water and chemical processing. Relying solely on groundwater or deep tube wells is often unsustainable and can lead to environmental penalties or depletion of local resources.
5. How do government policies in India influence site selection?
The Indian government often provides subsidies, tax holidays, or easier licensing for plants established in "No-Industry Districts" or Special Economic Zones (SEZs) to promote regional development. Engineers must verify zoning laws to ensure the plant's license is valid for the chosen district.
Conclusion:
Site selection is a complex but crucial decision that can significantly impact the success of a new plant. By carefully considering factors such as location, infrastructure, labor availability, and environmental impact, companies can make informed decisions that will lead to long-term operational efficiency and profitability.
A thorough and systematic approach, such as the weight-cum-rating method, can help businesses objectively evaluate potential sites and select the one that best aligns with their strategic goals. Remember, a well-chosen site is not just a location; it's a strategic advantage.
Kindly, follow my blogs on
Introduction to Piping Engineering
Process Technology Overview: From Concept to Operation
Piperack Design: Enhance Rack Lifespan for Plant Optimization
Piping Materials: Key Factors for SelectionUnderstanding Codes and Standards for Piping Materials
Plot Plan: Essential Guide to Industrial Plant Layout
Piping Interview Preparation: Site Selection, Plot Plans & GA Drawings
Please like, message and share if you feel all my blogs are beneficial, useful or helpful for you and for other also.
Thank you so much for following my blog…!! 🙏
See you all in the next coming blogs till then keep exploring piping field……!!
Have a great day today.... Keep smiling 😀 and God Bless You all…!!
To be continue……







Post a Comment